Mastering Advanced Vue.js Techniques
As you grow more comfortable with Vue.js and its ecosystem, you’ll encounter situations that require more specialized techniques. In this article, we’ll cover some advanced features that will allow you to tackle complex projects efficiently. We will explore dynamic components, mixins, render functions, and more, so you can master Vue.js and take your skills to the next level.
Dynamic Components in Vue.js

Dynamic components allow you to switch components dynamically without having to manually update your template. This is particularly useful for building flexible and reusable UI components.
Using component with v-bind
Vue provides the component element to dynamically switch components. You can pass a dynamic component name to this element using v-bind. Here's an example:
<component :is="currentComponent"></component>
In this case, the currentComponent is a dynamic value, and Vue will render the corresponding component. You can update the value of currentComponent based on the app’s state.
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
currentComponent: 'home'
},
components: {
home: HomeComponent,
about: AboutComponent
}
});
Mixins: Code Reusability and Composition
Mixins are a powerful feature of Vue that allow you to extract reusable logic into separate files. Mixins can contain data, methods, computed properties, and lifecycle hooks that are shared across components.
Using Mixins

To create a mixin, define the shared logic in a JavaScript file:
// myMixin.js
export default {
data() {
return {
message: 'Hello from mixin!'
};
},
methods: {
greet() {
console.log(this.message);
}
}
};
You can then import the mixin into your component:
import MyMixin from './myMixin';
new Vue({
el: '#app',
mixins: [MyMixin],
created() {
this.greet();
}
});
This approach allows you to organize and reuse code across multiple components, which is particularly helpful in large applications.
Render Functions for Fine-Grained Control
In Vue, you can use render functions to create components programmatically. This gives you complete control over the DOM structure and allows you to use dynamic rendering with JavaScript.
Example of a Render Function
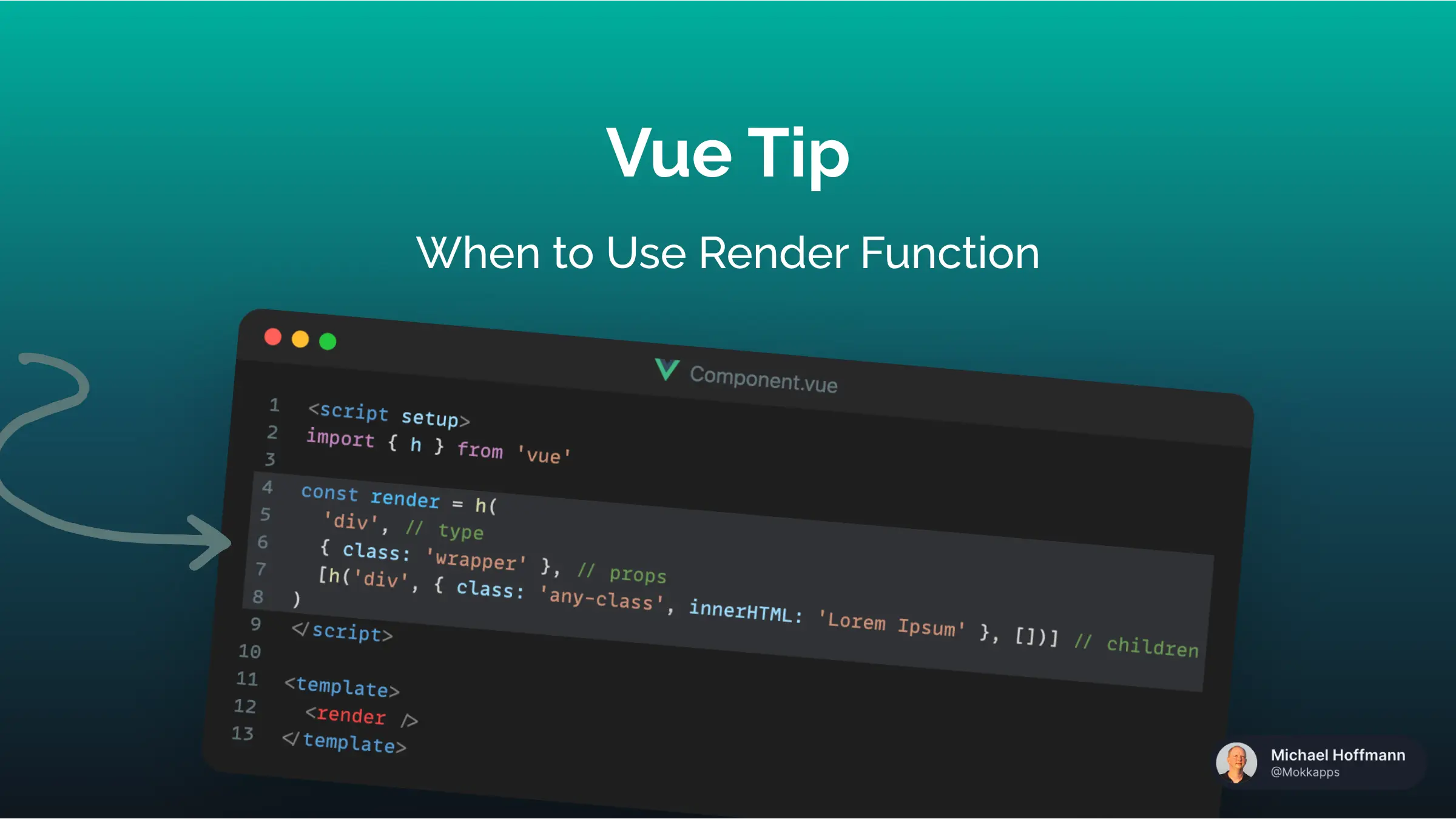
Here’s an example of how to define a render function in Vue:
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render(h) {
return h('div', { class: 'container' }, [
h('h1', 'Hello Vue!')
]);
}
});
The render function receives a createElement function (commonly abbreviated as h) that allows you to create virtual DOM nodes.
While most applications don’t require render functions, they can be extremely useful when building highly dynamic or complex components.
Scoped Slots for Flexible Component Design
Scoped slots are a powerful feature in Vue.js that allow you to pass dynamic content into child components with full access to their internal state. This makes components more flexible and reusable.
Using Scoped Slots
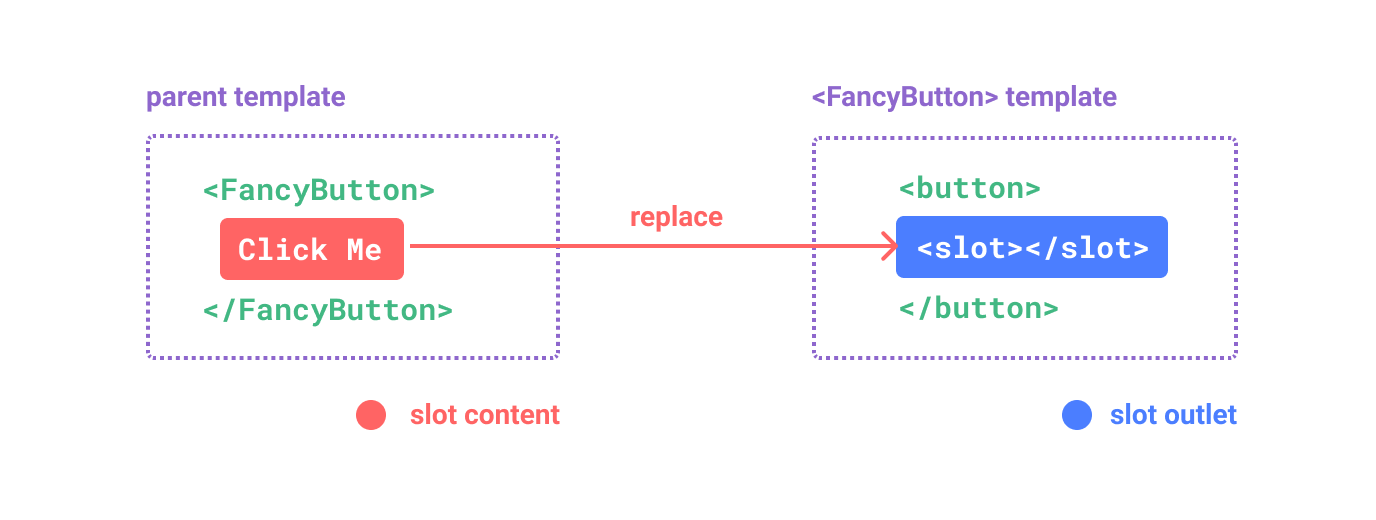
Here's an example where a parent component passes data to a child component via a scoped slot:
<child-component>
<template v-slot:default="slotProps">
<p>{{ slotProps.message }}</p>
</template>
</child-component>
In the child component, you can define the scoped slot like this:
Vue.component('child-component', {
template: `<slot :message="message"></slot>`,
data() {
return {
message: 'Hello from child component!'
};
}
});
Scoped slots provide a powerful way to create reusable components that can adapt based on their context.
Conclusion
Mastering advanced Vue.js techniques will significantly improve your ability to build complex, high-performance applications. By leveraging dynamic components, mixins, render functions, and scoped slots, you’ll be able to create maintainable, flexible, and scalable Vue apps. These tools not only enhance your productivity but also give you complete control over your application's behavior and structure.
Continue to explore Vue’s features, experiment with different approaches, and refine your skills. With the knowledge of these advanced concepts, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle any project and become a Vue.js expert.
