Advanced Vue.js Concepts for Beginners
After learning the basics of Vue.js, you may want to explore some more advanced features and concepts to enhance your development experience. This article will cover some of the more intricate parts of Vue, including custom directives, lifecycle hooks, and state management.
Custom Directives in Vue.js
Vue allows you to create custom directives to extend the functionality of the template syntax. Directives are prefixed with v-, such as v-bind or v-model. You can define your own directives to create custom behaviors.
Creating a Custom Directive

To create a custom directive, you use the Vue.directive method:
Vue.directive('focus', {
inserted: function (el) {
el.focus();
}
});
Now, you can use this directive in any template:
<input v-focus />
This directive automatically focuses on the input field when it is inserted into the DOM.
Vue.js Lifecycle Hooks
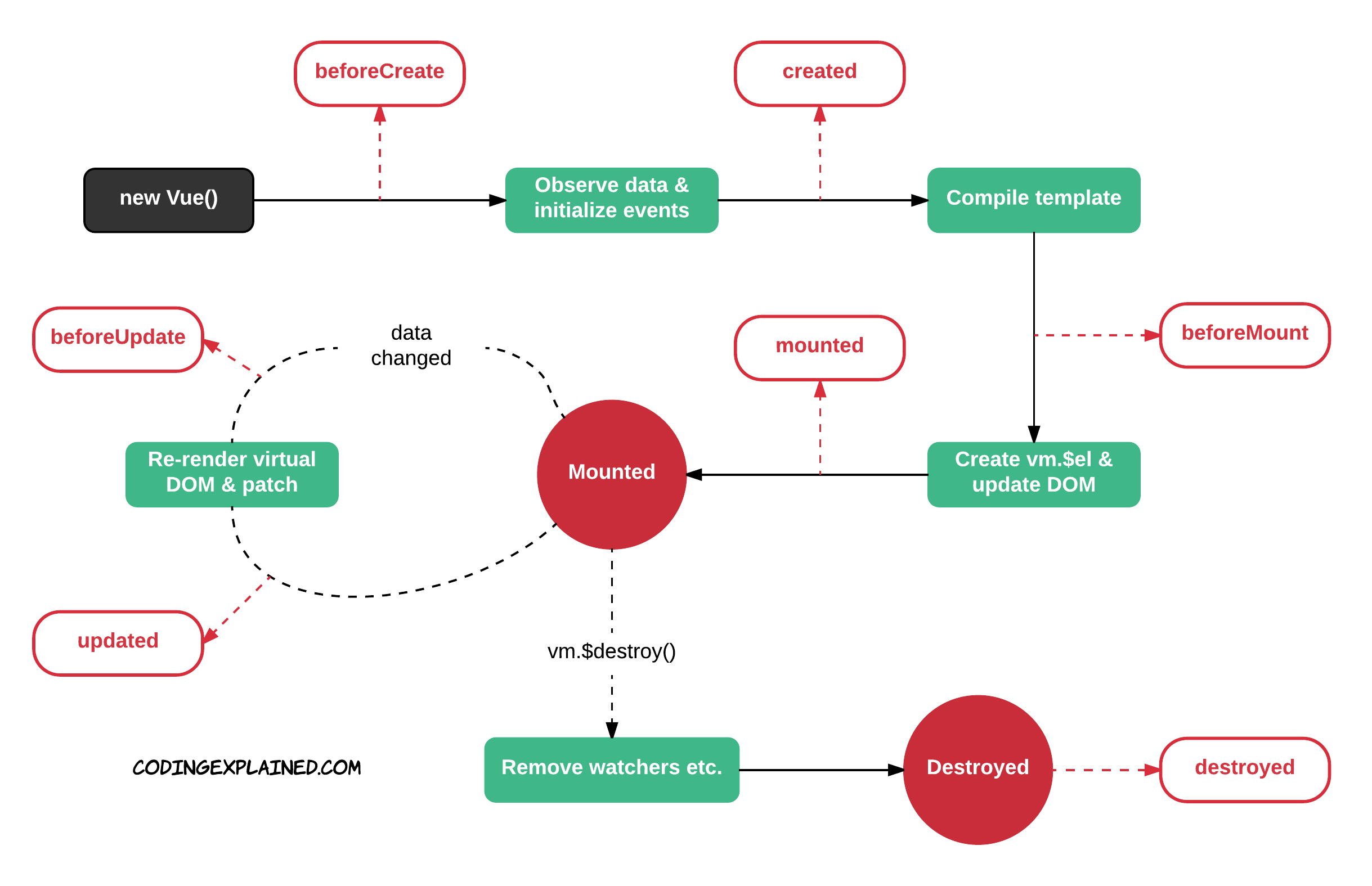
Vue provides several lifecycle hooks that allow you to run custom code at specific points during a component's life. These hooks give you control over the component as it is created, updated, or destroyed.
Common Lifecycle Hooks
created: Called when the component is created, but before it is mounted.mounted: Called after the component is mounted to the DOM.updated: Called after the component’s DOM has been updated.destroyed: Called when the component is destroyed.
Here’s an example that uses the mounted lifecycle hook:
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue.js!'
},
mounted() {
console.log('Component is mounted');
}
});
In this example, the message will be logged to the console once the component is mounted.
State Management in Vue.js

For larger applications, managing the state of your app can become complex. Vuex is a state management library for Vue.js that helps you manage your app’s state in a centralized store.
Setting Up Vuex
First, install Vuex if you haven’t already:
npm install vuex
Then, set up a basic Vuex store:
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++;
}
}
});
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
computed: {
count() {
return this.$store.state.count;
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.commit('increment');
}
}
});
Now, you can access and update the state using Vuex in any component.
Computed Properties vs Methods
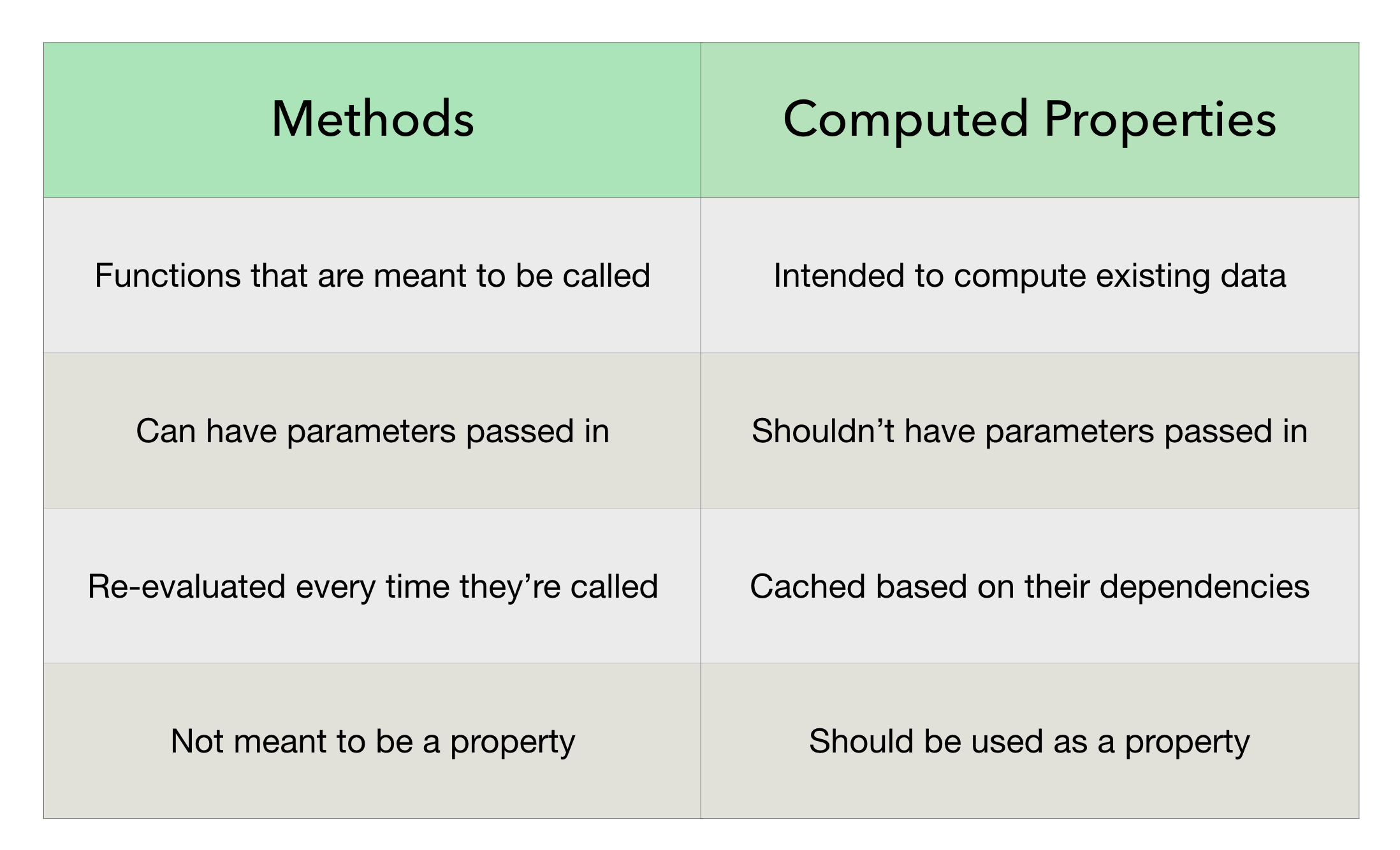
In Vue.js, both computed properties and methods allow you to define dynamic behavior. However, they differ in how they are evaluated.
- Computed Properties: They are cached based on their dependencies and only re-evaluated when necessary.
- Methods: They are re-evaluated every time the component re-renders.
Here’s an example:
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
a: 1,
b: 2
},
computed: {
sum() {
return this.a + this.b;
}
},
methods: {
calculateSum() {
return this.a + this.b;
}
}
});
While sum (computed) is cached and only recomputed when a or b changes, calculateSum (method) will run every time the component re-renders.
Conclusion
As you continue working with Vue.js, it’s important to dive deeper into more advanced concepts. Custom directives, lifecycle hooks, and state management with Vuex can significantly enhance your ability to build complex applications. With these tools at your disposal, you can create scalable, maintainable, and performant Vue apps.
By mastering these advanced features, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a Vue.js expert!
